TexAnASD - Text Analytics for ASD Risk Gene Predictions
 Abstract
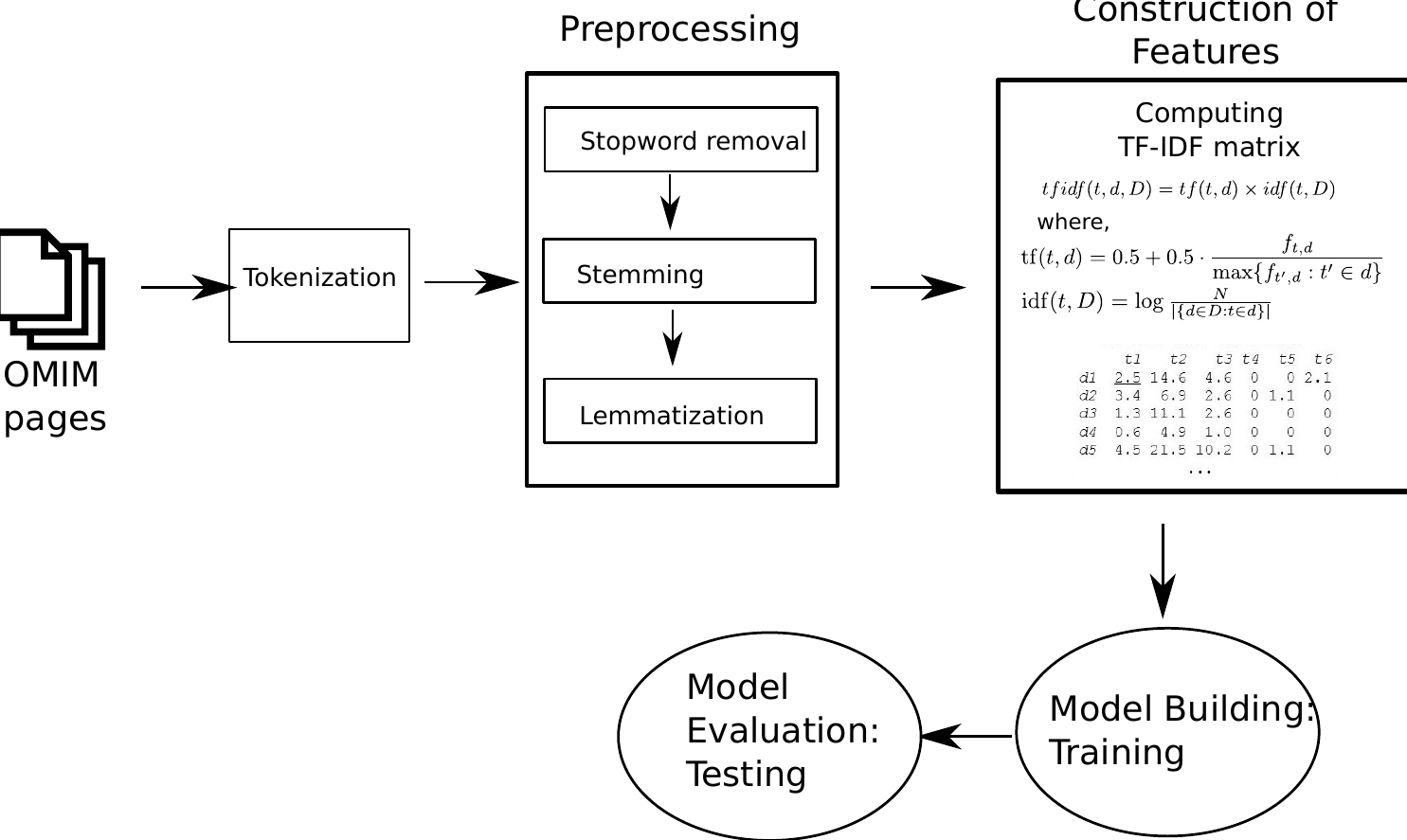
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is an extreme neurodevelopmental disease affecting 1 in every 59 children in the United States, and approximately 1\% of US population. The clinical traits of the disorder include noticeable deficits in social interactions, language development and in many cases very narrow and repetitive interests and behaviors. ASD is highly heritable genetic disease, but the known causes including the biomarkers associated with ASD form only the tip of the iceberg. Over the past decade extensive research on exome sequences revealed only about one hundred genetic biomarkers with very high confidence. Number of putative ASD causing genes is rapidly growing with the advent of new technologies while researchers are struggling now to assess which genes are the true causing genes. Manual curation of each of the long list of genes is a cumbersome process that requires huge amount of expert work-hours, and is therefore expensive. An in silico prediction method can assist the human experts to check only a short-list of genes that were filtered through a machine learning system. Most of the existing ASD gene prediction algorithms involve high-performance computing platform to analyze large-scale genetic data which is counter-intuitive to the actual benefit of using an in silico method in the first place. We propose TexAnASD, a text analytics based ASD gene prediction algorithm that only utilizes what we know about each gene that we learn from published literatures. The proposed method outperforms most of the state-of-the-art ASD associated gene prediction methods. Moreover, the method offers an inexpensive model than those of the other competing solutions in terms of computational complexity and running time. All source codes, dataset, predictions and functional insights are available here.
Abstract
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is an extreme neurodevelopmental disease affecting 1 in every 59 children in the United States, and approximately 1\% of US population. The clinical traits of the disorder include noticeable deficits in social interactions, language development and in many cases very narrow and repetitive interests and behaviors. ASD is highly heritable genetic disease, but the known causes including the biomarkers associated with ASD form only the tip of the iceberg. Over the past decade extensive research on exome sequences revealed only about one hundred genetic biomarkers with very high confidence. Number of putative ASD causing genes is rapidly growing with the advent of new technologies while researchers are struggling now to assess which genes are the true causing genes. Manual curation of each of the long list of genes is a cumbersome process that requires huge amount of expert work-hours, and is therefore expensive. An in silico prediction method can assist the human experts to check only a short-list of genes that were filtered through a machine learning system. Most of the existing ASD gene prediction algorithms involve high-performance computing platform to analyze large-scale genetic data which is counter-intuitive to the actual benefit of using an in silico method in the first place. We propose TexAnASD, a text analytics based ASD gene prediction algorithm that only utilizes what we know about each gene that we learn from published literatures. The proposed method outperforms most of the state-of-the-art ASD associated gene prediction methods. Moreover, the method offers an inexpensive model than those of the other competing solutions in terms of computational complexity and running time. All source codes, dataset, predictions and functional insights are available here.
Source Codes
- Github link to the project codes https://github.com/jpastorino/TexAnASD
Collaborators
- Javier Pastorino
- Ashis Kumer Biswas
News / Achievements
- IEEE BIBM 2019 - accepted at the workshop on Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence in Bioinformatics and Medical Informatics in the IEEE Bioinformatics and Biomedicine conference. (San Diego, CA, USA, November 18 - 21, 2019). Details of the venue